SEO: Updating Content for Higher Click-throughs
[ad_1]
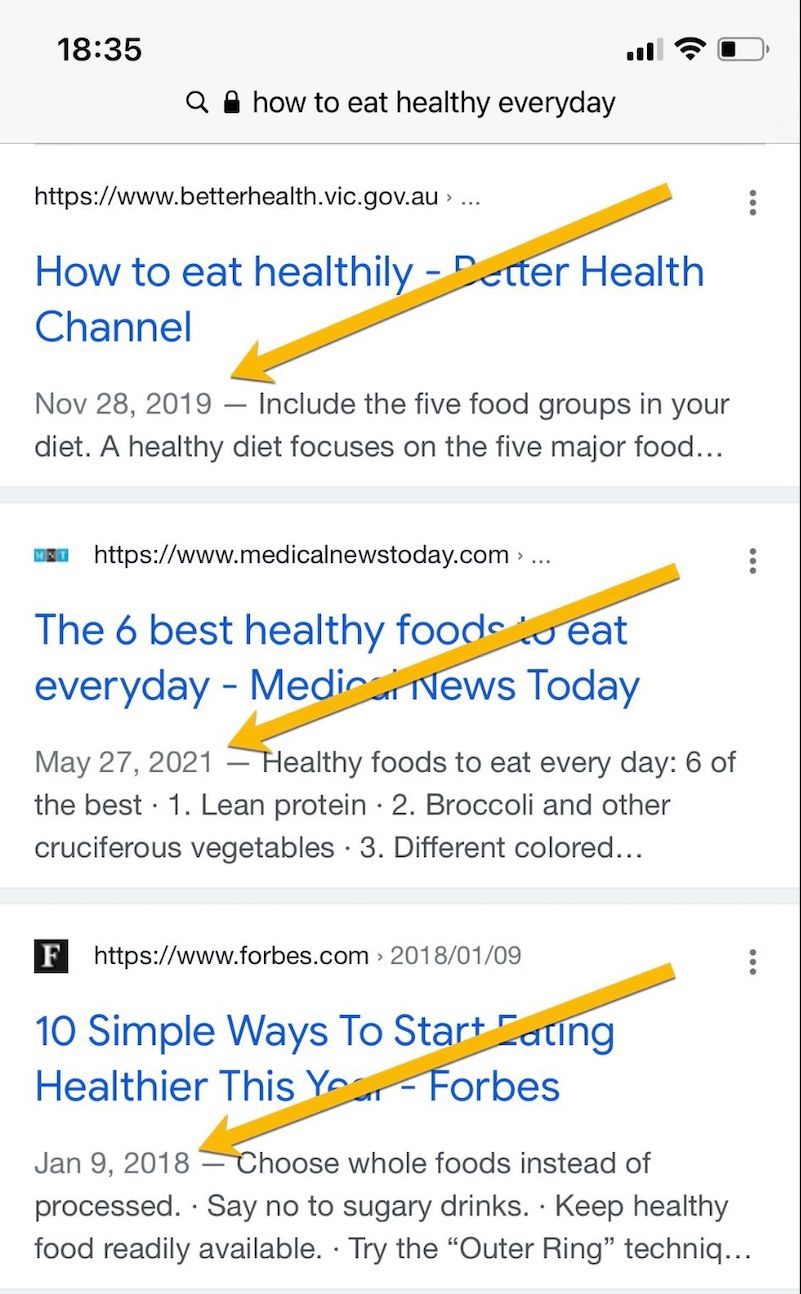
Google claims that it reveals dates in natural search snippets when its algorithm determines they’d be related and useful. In actuality, dates are extraordinarily frequent and have a huge impact on click-throughs.
I are likely to click on on newer outcomes. According to Ignite Visibility, a advertising agency, roughly 50% of searchers are like me: Dates in search snippets are both “vital” or “crucial” click-through elements.
Dates and search engine marketing
Google gives clear tips as to methods to talk dates to its algorithm:
- Select a typical date format and choose your time zone. WordPress, for instance, makes it straightforward.
- Use structured information resembling Schema.org to make it much more obvious. The Yoast WordPress plugin gives that choice.
- Together with a publish date and time will increase the probabilities of showing in Google Information and Google Discover.
Nevertheless it’s latest dates that drive clicks. What occurs when dates inside a search snippet are outdated? First, by no means conceal dates, even older ones. And keep away from stale dates for key content material by retaining it up to date.
Don’t conceal dates. Until it’s a static web page — e.g., About Us, Contact Us, Privateness Coverage — dates are useful to searchers. And Google will emphasize it if it helps a searcher. Transparency to Google builds belief, which drives rankings. Furthermore, eradicating older dates is pointless, in line with Google’s John Mueller in a Might 2021 tweet, stating “Even if you publish one thing with out a date, Google nonetheless retains time.”
Replace content material. If an outdated date in a search snippet hurts clicks, the most effective treatment is to replace the content material. That may even assist on-page engagement, as readers favor present information for many subjects.
Updating content material commonly is a key natural search tactic. By no means merely assign a brand new date to outdated, unchanged content material. Google requires a “substantial” edit, as follows:
If an article has been considerably modified, it might make sense to present it a recent date and time. Nonetheless, it’s in opposition to our tips to artificially freshen a narrative when the writer didn’t add vital info… It’s additionally in opposition to our tips to create a really barely up to date story from a beforehand printed one, then delete the outdated story and redirect to the brand new one.
A considerable change involves including new information, up to date citations, and whole rewrites of vital sections. After that, talk the change to Google and readers in one among two methods:
- Total rewrite. Change the publication date and push the web page to the highest of the archive. Don’t write a brand new article and redirect the outdated URL to the brand new one.
- Partial rewrite. Add an “Up to date on” be aware on prime of the article should you made minor adjustments, resembling just a few new paragraphs or choose information updates.
Google confirms that the entire date codecs under are acceptable. And utilizing Schema.org markup to make the dates clearer (to Google) is at all times a good suggestion.
- “Posted Feb 4, 2019”
- “Revealed February 4, 2019”
- “Final up to date: Feb 14, 2018”
- “Up to date Feb 14, 2019 8pm ET”
Which Snippets to Replace?
Not all content material is date-sensitive. Thus don’t repair what’s not damaged, assuming, once more, the content material stays legitimate.
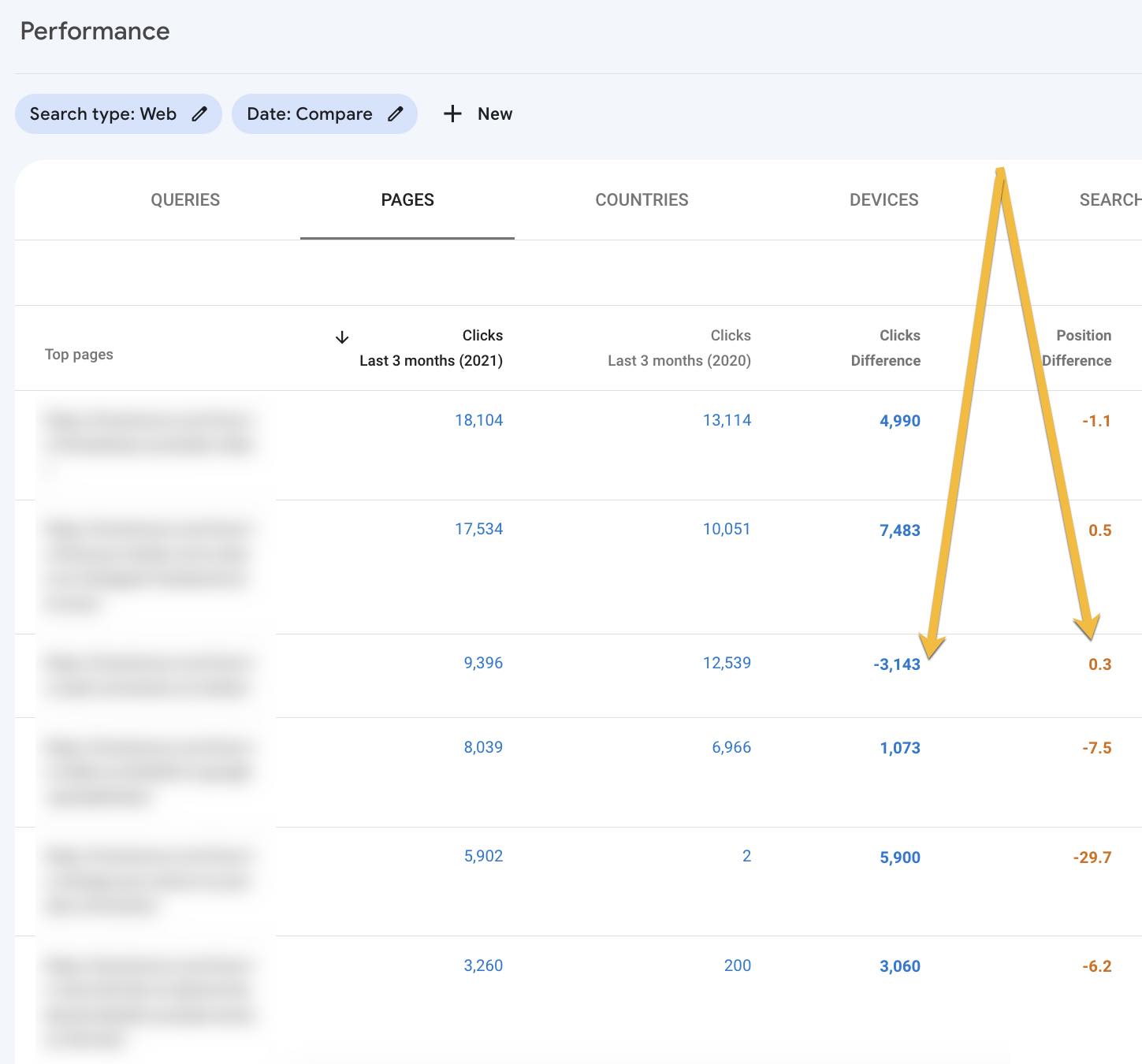
I take advantage of Google’s Search Console to find out the pages that might profit from an replace.
Within the Efficiency > Search outcomes tab, click on within the date vary filter (it normally defaults to 3 months), go to “Examine,” and choose “Examine final 3 months 12 months over 12 months.”
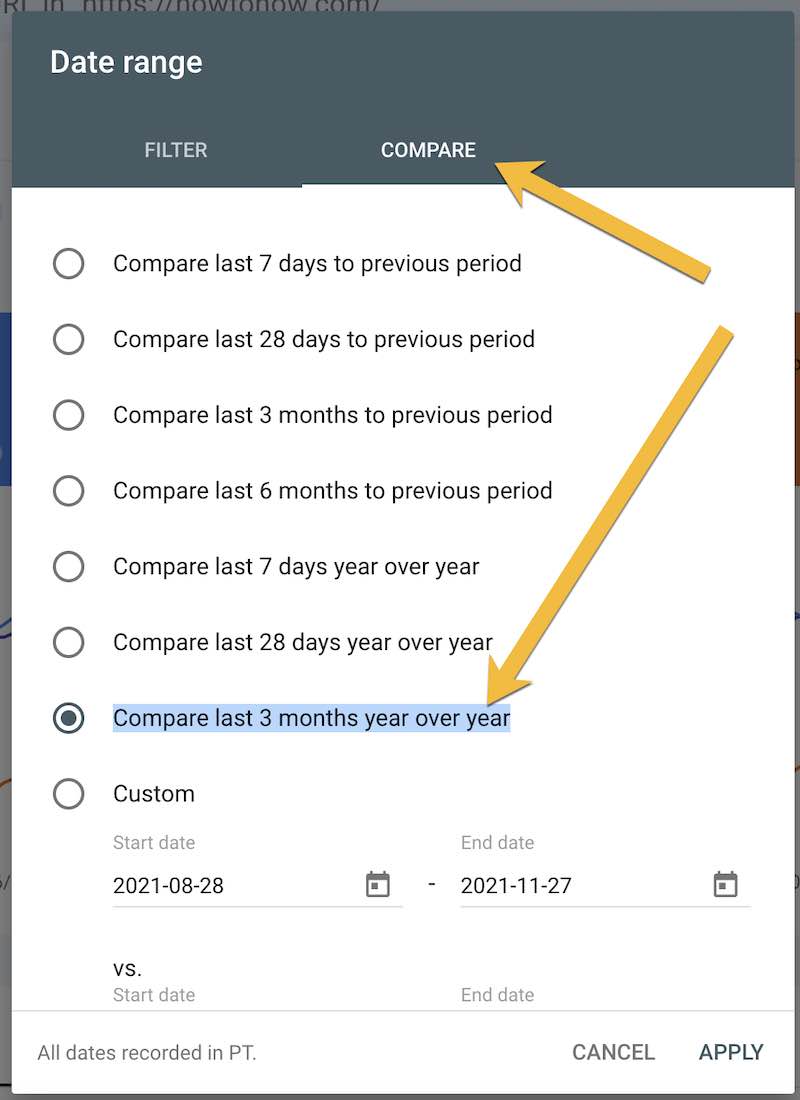
In Search Console, go to Efficiency > Search outcomes > Examine > Examine final 3 months 12 months over 12 months.
From there, click on “Pages” to determine URLs which have misplaced natural site visitors from the previous 12 months, particularly with no substantial place change. These are your greatest candidates for a refresh. Do that a couple of times a 12 months, relying on the amount of latest content material and whether or not it’s evergreen.
[ad_2]
Source link