The Fallacy of Data-driven Decisions
[ad_1]
Entrepreneurs and managers who lead rising corporations typically make vital selections primarily based on imperfect information and a intestine feeling.
Most, if not all, corporations search “data-driven” selections. When it launches a brand new product, updates its branding, or defines its focus, an organization wishes glorious market intelligence.
Sadly, glorious intelligence not often exists. Human bias impacts information interpretation. However we nonetheless need to make selections. To know the complexity, take into account a few decision-making frameworks.
Info-action Paradox
In enterprise, it’s typically the case that the extra public a market development, a chance, or a buyer phase, the much less freedom we now have to behave.
Because the authors of a latest Harvard Business Review article put it, when “information is broadly accessible…others see the identical alternatives and dangers and reply to them.”
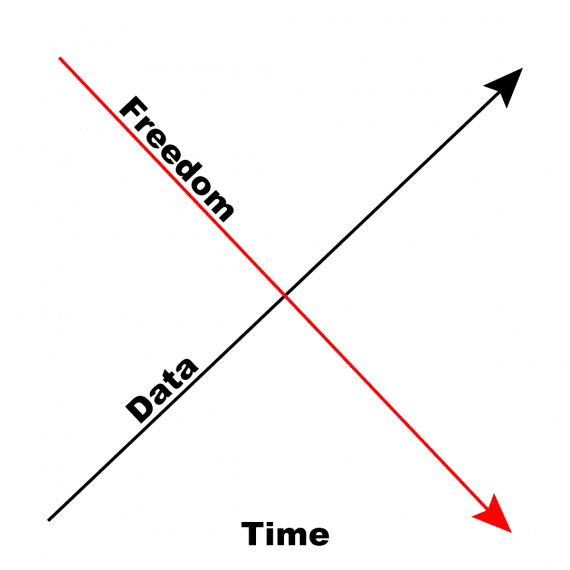
The data-action paradox implies that the liberty to behave on data and its public availability are inverse.
A brand new entrepreneur can decide primarily based on comparatively sparse public information, an inkling of a development. She has little data however loads of freedom to decide on.
An incumbent enterprise should typically await extra public information since its managers can not often act unilaterally however should get buy-in from superiors, friends, and subordinates. These leaders should work by a technique of coaxing and convincing, typically ready for additional data. Incessantly, such corporations have extra data for strategic selections however comparatively much less freedom to behave since rivals will even concentrate on the chance.
This paradox would possibly lead some managers to behave rapidly, forward of rivals.
Diderot Impact
Choices primarily based on little-known information might result in alternative, however they require executives to belief their intestine stemming from experiences and emotions.
Human psychology turns into an element.
Right here’s a real-life instance. A software-as-a-service firm within the technique of repositioning itself determined to deal with mid-sized prospects. It made the selection with comparatively little public data. However as a result of it’s smallish, the corporate had vital freedom to behave.
The choice impacted a number of managers and their departments.
It prompted one supervisor to conclude she should cease concierge assist to twenty of the corporate’s largest and most worthwhile prospects since these enterprises had been now not the main target.
Ignoring very worthwhile prospects as a result of they don’t match with the corporate’s perceived technique is harking back to the Diderot Impact in shopping for.
Denis Diderot was an 18th-century French thinker. Amongst his many influential works is a lean essay a couple of new pink gown, titled “Regrets for my Previous Dressing Robe, or A warning to those that have extra style than fortune.”
Diderot received a elaborate new gown and in the end redecorated his whole research with costly artwork and furnishings as a result of the high quality gown made the room really feel uncoordinated and ugly. Diderot was much less pleased regardless of the brand new possessions.
Within the late Eighties, cultural anthropologist and creator Grant McCracken used Diderot’s essay as an instance two human tendencies, which he collectively known as “the Diderot Impact.”
- Buy selections are usually not all the time rational; we purchase issues that match our identification.
- A brand new possession, like Diderot’s gown, can redefine our identification, prompting us to make subsequent and pointless purchases that conform to it.
The BBC has an excellent explainer video describing the Diderot Effect.
Extra just lately, creator James Clear used the Diderot Impact in his ebook “Atomic Habits” to explain how private identification impacts alternative and routine.
Thus the Diderot Impact describes shopping for habits and behavior formation, but it surely might additionally have an effect on enterprise selections.
Therefore the SaaS supervisor was prepared to cease servicing 20 of an organization’s greatest prospects as a result of that call matched her notion of the enterprise’s identification.
Steadiness
The data-action paradox and the Diderot Impact are current when an organization makes strategic decisions.
The data-action paradox implies that enterprise leaders ought to act once they have extra freedom, making the most of alternatives earlier than their rivals.
However the Diderot Impact implies that we should always pause to grasp what motivates these selections.
So right here is the excellent news. Enterprise leaders who acknowledge these forces can account for them, hanging a steadiness. When contemplating a strategic resolution, take a look at each: the info and the influences.
[ad_2]
Source link

